Physics A: Problem Set 22: The particle nature of light
recommended reading
| High Marks: | 5:1–5:5 |
| Barron's Let's Review: | 13.1–13.4 |
| physics.info: | Photoelectric effect |
| Wikipedia: | Photoelectric effect, Photon |
| HyperPhysics: | Photoelectric effect, Wave-particle duality |
| Khan Academy: | Photoelectric effect |
| Mr. Machado: | 01 Photon Energy and the Photoelectric Effect |
classwork
- The Balmer series is a set of wavelengths emitted by excited hydrogen atoms. Complete the following table for the four visible wavelengths in the Balmer series identified by the Greek letters α (alpha), β (beta), γ (gamma), and δ (delta).
characteristic α β γ δ wavelength (nm) 656 nm 486 nm 434 nm 410 nm frequency (Hz) energy per photon (J) energy per photon (eV) color One column in the table above has been highlighted. To receive credit for this assignment you must show the work for the answers in that column below. Fill in the remaining columns using values you calculate somewhere else, or values that were calculated by someone else that you have good reason to believe are correct. Turn this completed page in at the end of the period.
- Show the work you did to compute the frequency in hertz for the photon in your highlighted column below. (Be sure to include an equation and substitution of values with units.)
- Show the work you did to compute the energy in joules for the photon in your highlighted column below. (Be sure to include an equation and substitution of values with units.)
- Show the work you did to compute the energy in electron-volts for the photon in your highlighted column below. (Be sure to include an equation and substitution of values with units.)
- There is no work to show for this part. Just state the color of the photon in your highlighted column below.
Solutions.
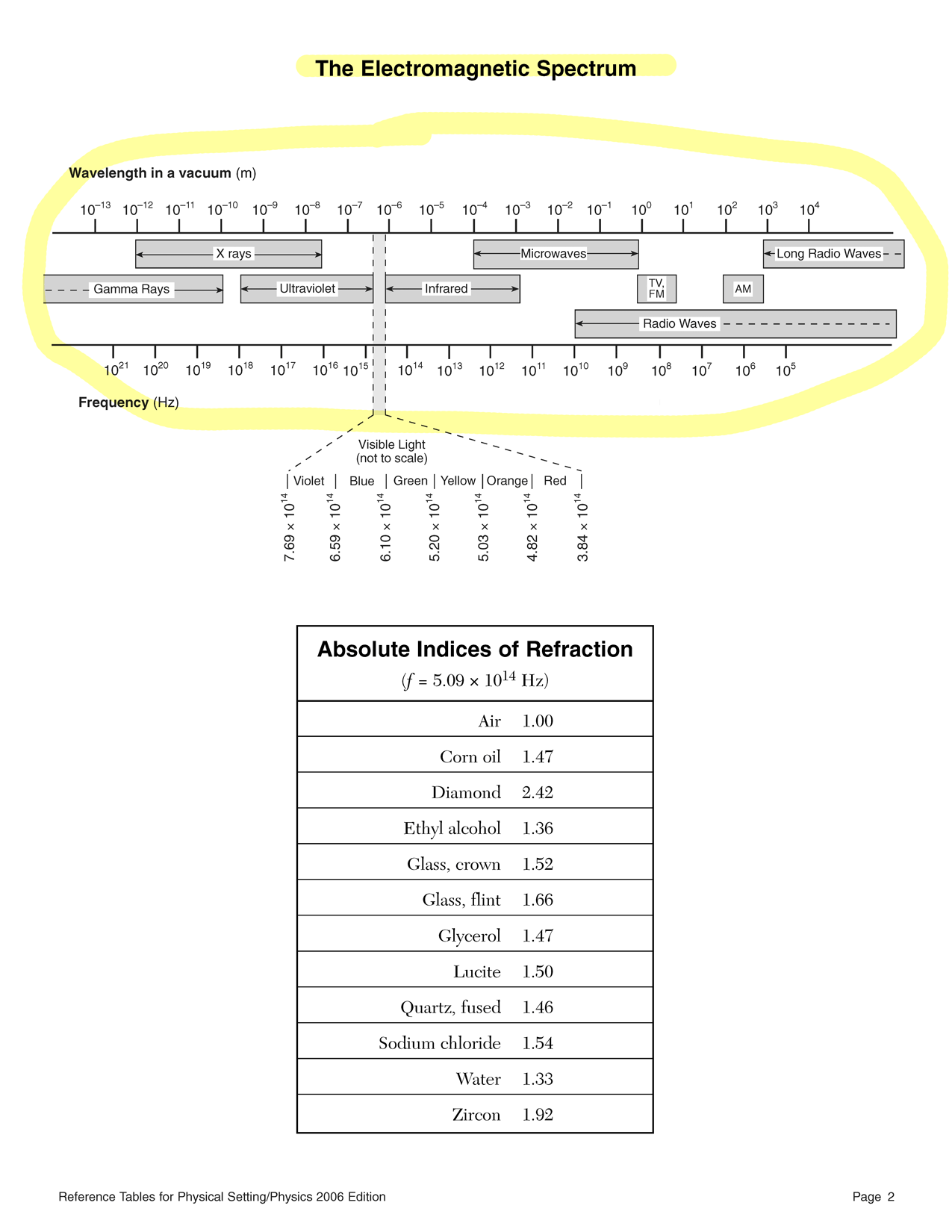
characteristic α β γ δ wavelength (nm) 656 nm 486 nm 434 nm 410 nm frequency (Hz) 4.57 × 1014 Hz 6.17 × 1014 Hz 6.91 × 1014 Hz 7.32 × 1014 Hz energy per photon (J) 3.03 × 10−19 J 4.09 × 10−19 J 4.58 × 10−19 J 4.85 × 10−19 J energy per photon (eV) 1.90 eV 2.56 eV 2.86 eV 3.03 eV color red blue violet violet - Frequency is computed using the wave speed equation and the speed of light in a vacuum (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s).
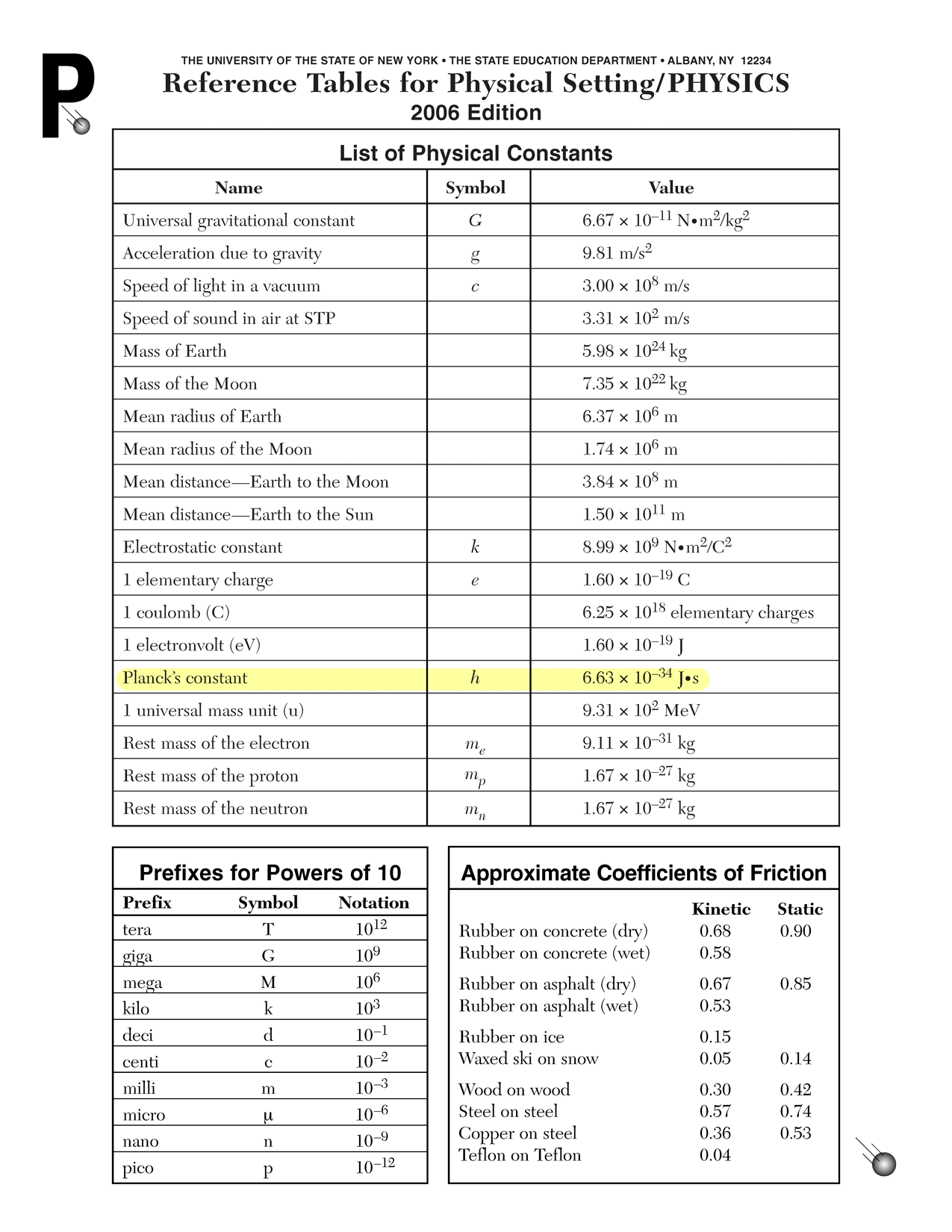
f = c ⇐ c = fλ λ - Energy per photon in joules is computed using Planck's relationship and Planck's constant (h = 6.63 × 10−34 J s).
E = hf
- To convert from joules to electronvolts, divide the energy in joules by the elementary charge in coulombs (q = e = 1.60 × 10−19 C).
V = E q - Color is found using your friendly neighborhood reference tables. If you don't have a reference table, I hear there is this website called Google that can help you find one.
homework
- Complete the following table for four different types of electromagnetic radiation.
characteristic E1 E2 E3 E4 energy per photon (eV) 100 eV 103 eV 106 eV 109 eV energy per photon (J) frequency (Hz) wavelength (m) type of radiation One column in the table above has been highlighted. To receive credit for this assignment you must show the work for the answers in that column below. Fill in the remaining columns using values you calculate somewhere else (like the other side of this page), or values that were calculated by someone else that you have good reason to believe are correct. Turn this completed page after 10 minutes of discussion with other classmates at the begining of class on the day when this is due.
- Show the work you did to compute the energy in joules for the photon in your highlighted column below. (Be sure to include an equation and substitution of values with units.)
- Show the work you did to compute the frequency in hertz for the photon in your highlighted column below. (Be sure to include an equation and substitution of values with units.)
- Show the work you did to compute the wavelength in meters for the photon in your highlighted column below. (Be sure to include an equation and substitution of values with units.)
- There is no work to show for this part. Just state the type of radiation of the photon in your highlighted column below.
Solutions.
characteristic E1 E2 E3 E4 energy per photon (eV) 100 eV 103 eV 106 eV 109 eV energy per photon (J) 1.60 × 10−19 J 1.60 × 10−16 J 1.60 × 10−13 J 1.60 × 10−10 J frequency (Hz) 2.42 × 1014 Hz 2.42 × 1017 Hz 2.42 × 1020 Hz 2.42 × 1023 Hz wavelength (m) 1.24 × 10−6 m 1.24 × 10−9 m 1.24 × 10−12 m 1.24 × 10−15 m type of radiation infrared ultraviolet,
or x-rayx-ray, or
gamma raygamma ray To convert from electronvolts to joules, multiply the voltage in volts by the elementary charge in coulombs (q = e = 1.60 × 10−19 C).
E = qV ⇐ V = E q Frequency is computed using Planck's equation and Planck's constant (h = 6.63 × 10−34 J s).
f = E ⇐ E = hf h Wavelength is computed using the wave speed equation and the speed of light in a vacuum (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s).
λ = c ⇐ c = fλ f The type of radiation can be found in the spectrum chart of your choice.